Abstract
Introduction:
Patients (pts) with limited stage (LS) aggressive large B-cell lymphoma (ALBCL) comprise 30-40% of ALBCLs and are usually treated with R-CHOP with or without consolidative involved field radiation therapy (IFRT). In pts with ALBCL, cytogenetic studies have identified a subset with high-risk disease who harbor MYC rearrangement (MYC-R) with or without BCL2 (BCL2-R) and/or BCL6 (BCL6-R) rearrangements. This has led to the adoption of intensive induction strategies in this population; however, it is unclear if such an approach is necessary in limited stage disease.
Methods:
We conducted a multi-center (15 US academic centers) retrospective study of MYC-R LS-ALBCL pts with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and high-grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBL) morphology. LS was defined by stage I and II confined to a single radiation field as determined by the treating center. Pts diagnosed between 1/1/2005 and 3/1/2017 were included. All pts received either R-CHOP or more intensive immuno-chemotherapy (IIC) (i.e. R-DA-EPOCH, R-hyperCVAD/MA, or R-CODOX-M/IVAC) with or without IFRT. Baseline demographic, clinical, laboratory, pathology and outcomes data was collected by retrospective chart review. Stage-modified IPI (sm-IPI) score was calculated [stage II (vs 1), age >60, elevated LDH, and ECOG performance status ≥ 2]. Differences in overall response rate (ORR), complete remission (CR) rate, 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were compared in pts treated with R-CHOP vs IIC and in pts treated with IFRT vs no IFRT.
Results:
A total of 142 pts with MYC-R LS-ALBCL were identified, of which 105 fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Baseline characteristics included: median age 65 yrs (range 21-85), 66% male; 14% stage I, 32% stage IE, 28% stage II, 26% stage IIE disease; 17% bulky, 58% extra-nodal, 15% transformed disease, 40% elevated LDH. The majority of pts (70%) had germinal center B-cell phenotype. Eighty-two pts had data on BCL2-R and BCL6-R, of which 41 (50%) had double-hit lymphoma (DHL), including 4 pts with triple-hit lymphoma.
Forty-five pts (43%) received R-CHOP, of which 56% had IFRT. Sixty pts (57%) received IIC, of which 42% had IFRT. R-DA-EPOCH was the most common IIC regimen used (85%), followed by R-hyperCVAD/MA (12%). Age (p=0.38), stage (p=0.32), extra-nodal disease (p=0.84), LDH (p=0.09), sm-IPI (p=0.24), morphology (p=0.44) and double-hit status (p=1.00) were similar between pts receiving R-CHOP and IIC. Median no. of cycles (NOC) (6 vs 6) and proportion of pts who received IFRT (56% vs 42%, p=0.17) did not differ in the 2 groups. Median NOC were lower in IFRT vs no IFRT group (4 vs 6; p=0.02). Pts receiving IIC (vs. R-CHOP) were more likely to undergo CNS prophylaxis (CNS-P) (75% vs 29%, p<0.001). No. of pts receiving CNS-P were similar in DHL vs MYC-R only (64% vs 49%; p=0.23).
ORR was 90% (83% CR, 7% PR). Pts with DHL were less likely to achieve a CR compared to pts with MYC-R only (73% vs 98%; p=0.011). CR rate was higher in the IFRT vs no-IFRT group (92% vs. 75%, p=0.028). In the 27 pts who had relapsed/refractory disease, distant relapses were more common in the IFRT vs no-IFRT group (87% vs 33%, p=0.007).
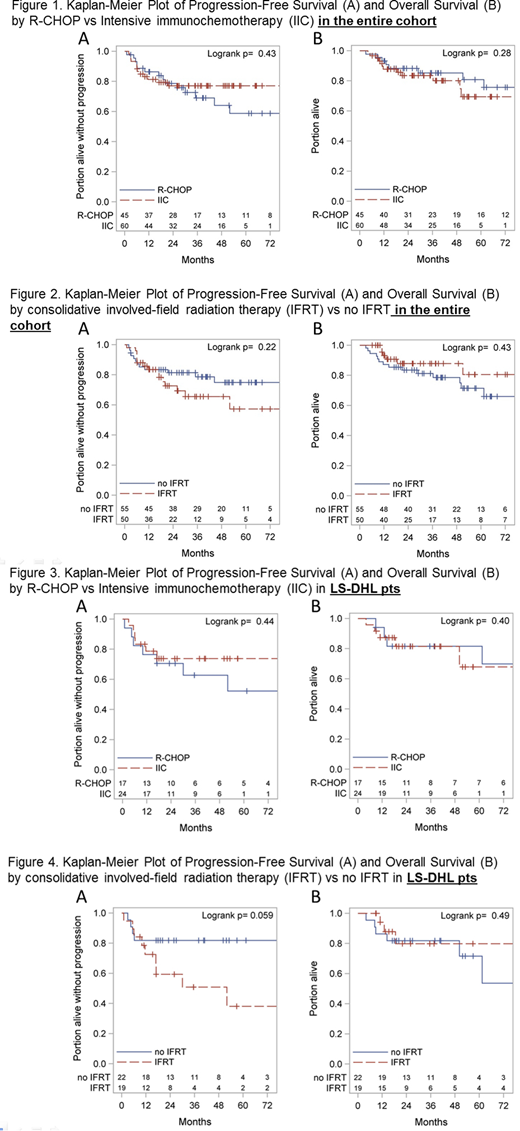
Median follow-up was 3.2 yrs; 35 (33%) pts progressed or died. Of the 23 deaths, 15 were due to progressive lymphoma, 1 due to treatment-related toxicity and 7 due to unrelated causes. 2-year PFS and OS were 78% and 86% for the entire cohort and 72% and 82% respectively for DHL pts. Sm-IPI ≥ 2 (HR: 2.81, p=0.02) and age ≥ 70 (HR: 4.07, P<0.001) were associated with inferior OS. Stage, extra-nodal disease, morphology, LDH and double hit status did not affect survival. PFS and OS were similar across treatment groups (IFRT vs no IFRT, R-CHOP vs IIC) in the entire cohort (Figures 1 and 2) and in DHL pts (Figures 3 and 4). Use of CNS-P was not associated with improved PFS (HR: 0.57 [95% CI: 023, 1.43]) or OS (HR 0.98 [95% CI: 0.34, 2.85]).
Conclusions:
Outcomes of MYC-R LS-ALBCL pts are excellent with 2-year PFS and OS of 78% and 86% respectively. There was no benefit of choosing IIC over R-CHOP or using CNS prophylaxis in pts with MYC-R LS-ALBCL and LS-DHL in our study. While IFRT was effective in inducing CRs and preventing local relapses, distant relapses limited its benefit. Pts with LS-DHL had lower CR rates with similar PFS and OS when compared to those with MYC-R as the sole cytogenetic abnormality. Longer follow up is needed to assess the impact of upfront treatment strategies on late relapses.
Landsburg:Takeda: Consultancy; Curis: Consultancy, Research Funding. Maddocks:Teva: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Pharmacyclics/Janssen: Honoraria; Novartis: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding. Advani:Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals: Other: Consultancy/Advisory Role; Cell Medica: Other: Consultancy/Advisory Role; Janssen Pharmaceutical: Other: Institutional Research Support; Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Other: Institutional Research Support; Merck: Other: Institutional Research Support; Kyowa: Other: Consulting/Advisory Role; Celgene: Other: Institutional Research Support; Roche/Genentech: Other: Consultancy/Advisory Role, Institutional Research Support; Takeda: Other: Consultancy/Advisory Role; Gilead/Kite: Other: Consultancy/Advisory Role; Autolus: Other: Consultancy/Advisory Role; AstraZeneca: Other: Consultancy/Advisory Role; Seattle Genetics: Other: Consultancy/Advisory role, Institutional Research Support; Bristol Myers Squibb: Other: Consultancy/Advisory role and Institutional Research Support; Forty Seven, Inc: Other: Institutional Research Support; Pharmacyclics: Other: Institutional Research Support; Agensys: Other: Institutional Research Support; Kura: Other: Institutional Research Support; Infinity: Other: Institutional Research Support; Millenium: Other: Institutional Research Support. Barta:Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck, Takeda, Celgene, Seattle Genetics, Bayer: Research Funding. Vose:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding; Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Epizyme: Honoraria; Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Incyte Corp.: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Legend Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Cohen:Takeda: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Millennium: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BioInvent: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Infinity Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Karmali:AstraZeneca: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Speakers Bureau. Mehta:Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Kite: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Merck: Research Funding; Spectrum: Consultancy; Epizyme: Research Funding; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy; Carevive: Other: Patient engagement; Medpage: Other: Medical website. Olszewski:Spectrum Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Hill:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal